Holistic Cloud Security Defense In-Depth Strategy
Expired A Holistic Cloud Security Defense-In-Depth (DiD) Strategy is a multi-layered approach designed to protect cloud environments by mitigating threats at multiple levels: data, applications, endpoints, and networks. As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, they encounter security challenges such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and misconfigurations. Unlike traditional IT security, cloud security demands a dynamic and adaptive strategy that incorporates the shared responsibility model, Zero Trust principles, automated threat detection and risk mitigation.
A Holistic Cloud Security Defense-In-Depth (DiD) Strategy is a multi-layered approach designed to protect cloud environments by mitigating threats at multiple levels: data, applications, endpoints, and networks. As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, they encounter security challenges such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and misconfigurations. Unlike traditional IT security, cloud security demands a dynamic and adaptive strategy that incorporates the shared responsibility model, Zero Trust principles, automated threat detection and risk mitigation.
Cloud Security
Expired Cloud security refers to the set of practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud computing environments. It focuses on safeguarding cloud resources from unauthorized access, data breaches, data loss, and other security risks. Cloud security is essential because cloud computing involves storing and processing data and running applications on shared infrastructure and platforms provided by a third-party cloud service provider. This shared nature introduces unique security challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services.
Cloud security refers to the set of practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud computing environments. It focuses on safeguarding cloud resources from unauthorized access, data breaches, data loss, and other security risks. Cloud security is essential because cloud computing involves storing and processing data and running applications on shared infrastructure and platforms provided by a third-party cloud service provider. This shared nature introduces unique security challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services.
Automated Security Testing in CI/CD Pipeline
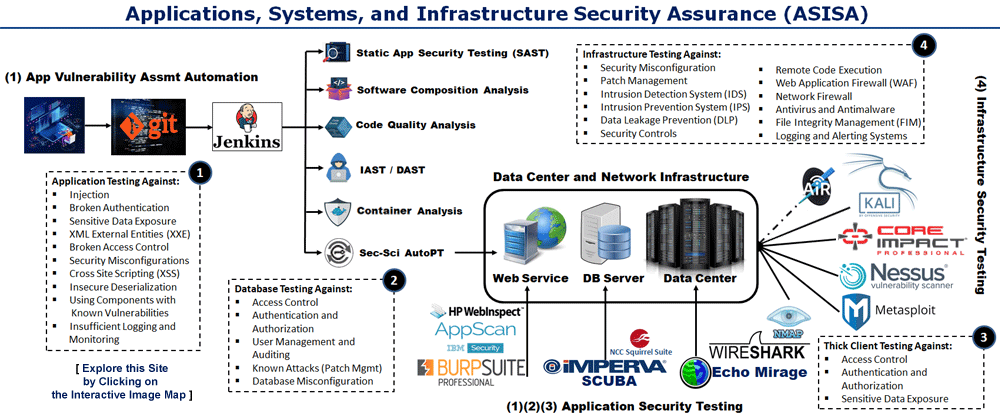
Expired Automated security testing in a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline, embraced by the DevSecOps approach, integrates various security testing practices into the software development process. It combines several automated security testing techniques to identify and address potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the application code before it is deployed to production. By incorporating automated security testing practices into the CI/CD pipeline with DevSecOps, organizations can proactively address security risks, reduce the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities, and accelerate the delivery of secure software.
Automated security testing in a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline, embraced by the DevSecOps approach, integrates various security testing practices into the software development process. It combines several automated security testing techniques to identify and address potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the application code before it is deployed to production. By incorporating automated security testing practices into the CI/CD pipeline with DevSecOps, organizations can proactively address security risks, reduce the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities, and accelerate the delivery of secure software.
Zero Trust Architecture
Expired Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework and approach that challenges the traditional perimeter-based security model. It is based on the principle of "never trust, always verify" and operates under the assumption that no user or device should be automatically trusted, whether they are inside or outside the organization's network perimeter. In a Zero Trust Architecture, every user, device, and network resource is treated as potentially untrusted and requires continuous verification and authentication. The key concept is to authenticate and authorize access based on multiple factors, such as user identity, device health, location, and behavior, before granting access to resources.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework and approach that challenges the traditional perimeter-based security model. It is based on the principle of "never trust, always verify" and operates under the assumption that no user or device should be automatically trusted, whether they are inside or outside the organization's network perimeter. In a Zero Trust Architecture, every user, device, and network resource is treated as potentially untrusted and requires continuous verification and authentication. The key concept is to authenticate and authorize access based on multiple factors, such as user identity, device health, location, and behavior, before granting access to resources.
Penetration Testing
Expired Penetration Testing (PenTest) is a structured approach to probing and evaluating the security posture and model of a product. It involves a combination of off-the-shelf tools, custom tools, and assessment workflows, some of which are derived from open-source standards like OWASP. The primary objective is to thoroughly test the live product and identify potential attack vectors that could lead to exploits or vulnerabilities. The scope of testing can encompass the entire product functionality or specific functionalities in a new or updated release. Penetration testing applies to various types of products, ranging from hardware, firmware, and appliances to web-based software and RESTful API platforms.
Penetration Testing (PenTest) is a structured approach to probing and evaluating the security posture and model of a product. It involves a combination of off-the-shelf tools, custom tools, and assessment workflows, some of which are derived from open-source standards like OWASP. The primary objective is to thoroughly test the live product and identify potential attack vectors that could lead to exploits or vulnerabilities. The scope of testing can encompass the entire product functionality or specific functionalities in a new or updated release. Penetration testing applies to various types of products, ranging from hardware, firmware, and appliances to web-based software and RESTful API platforms.
NSA and CISA Kubernetes Hardening Guide
Expired The National Security Agency (NSA) and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Kubernetes Hardening Guide is a resource that provides detailed recommendations and best practices for securing Kubernetes clusters. This guide is developed by the U.S. government agencies to help organizations enhance the security posture of their Kubernetes environments, following industry standards and security principles. The NSA and CISA Kubernetes Hardening Guide, organizations can implement robust security practices in their Kubernetes clusters, reducing vulnerabilities, and enhancing the defense against cyber threats.
The National Security Agency (NSA) and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Kubernetes Hardening Guide is a resource that provides detailed recommendations and best practices for securing Kubernetes clusters. This guide is developed by the U.S. government agencies to help organizations enhance the security posture of their Kubernetes environments, following industry standards and security principles. The NSA and CISA Kubernetes Hardening Guide, organizations can implement robust security practices in their Kubernetes clusters, reducing vulnerabilities, and enhancing the defense against cyber threats.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
Expired Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a cybersecurity approach and practice that focuses on proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating security threats and vulnerabilities across an organization's technology infrastructure in an ongoing and real-time manner. CTEM is designed to provide organizations with the ability to continuously monitor and respond to threats, thereby reducing the attack surface and improving overall cybersecurity posture. In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, threat actors continually adapt, necessitating organizations to streamline controls and deploy security patches promptly.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a cybersecurity approach and practice that focuses on proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating security threats and vulnerabilities across an organization's technology infrastructure in an ongoing and real-time manner. CTEM is designed to provide organizations with the ability to continuously monitor and respond to threats, thereby reducing the attack surface and improving overall cybersecurity posture. In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, threat actors continually adapt, necessitating organizations to streamline controls and deploy security patches promptly.