Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a cybersecurity approach and practice that focuses on proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating security threats and vulnerabilities across an organization's technology infrastructure in an ongoing and real-time manner. CTEM is designed to provide organizations with the ability to continuously monitor and respond to threats, thereby reducing the attack surface and improving overall cybersecurity posture.
How to Manage Cybersecurity Threats: Addressing the Growing Need for Continuous Threat Exposure Management
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, threat actors continually adapt, necessitating organizations to streamline controls and deploy security patches promptly. However, these reactive measures alone are insufficient to curtail future threats. What organizations require is a comprehensive Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) program designed to identify and prioritize threats that pose the greatest risk to their business. Establishing such a program entails a structured five-step approach.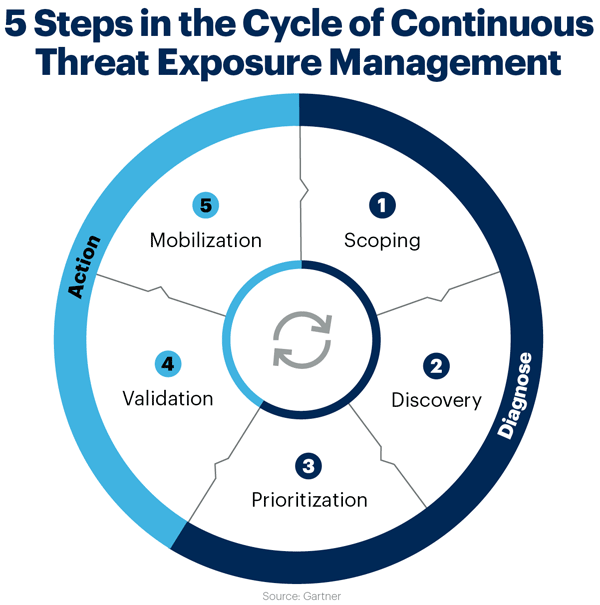
Step 1: Define the Scope of Cybersecurity Exposure, Starting with External and SaaS Threats
Commence by defining your organization's "attack surface," encompassing vulnerable entry points and assets. This goes beyond the typical focus of conventional vulnerability management programs. Consider not only traditional devices and applications but also less tangible elements like corporate social media accounts, online code repositories, and integrated supply chain systems.
Step 2: Develop a Discovery Process for Assets and Their Risk Profiles
While many discovery processes initially focus on areas of the business that were identified during scoping (Step No. 1), they should proceed to identify visible and hidden assets, vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other risks. It's important to distinguish between scoping and discovery to avoid common pitfalls. The true measure of success is not the volume of discovered assets and vulnerabilities but rather the accuracy of scoping based on business risk and potential impact.
Step 3: Prioritize Threats Most Likely to Be Exploited
The objective here is not to address every single security issue but to prioritize effectively. Consider factors such as urgency, severity, the availability of compensating controls, tolerance for residual attack surface, and the level of risk posed to the organization. Focus on creating a treatment plan that targets high-value assets of the business.
Step 4: Validate Attack Scenarios and System Responses
Begin by confirming the exploitability of vulnerabilities and assessing potential attack pathways to critical assets. Verify if the existing response plans are sufficiently agile and robust to protect the business. Equally important is gaining consensus among all stakeholders on the triggers that warrant remediation. By 2026, organizations aligning their security investments with a continuous exposure management program will be three times less likely to experience a breach.
Step 5: Mobilize Resources and Processes
While automated remediation holds promise, complete reliance on it is not prudent, especially for complex or sensitive issues. Instead, communicate your CTEM plan effectively to both the security team and business stakeholders, ensuring it is well-understood. The aim of this "mobilization" effort is to facilitate the operationalization of CTEM findings by removing barriers to approvals, streamlining implementation processes, and expediting mitigation deployments. In particular, document cross-team approval workflows to enhance efficiency and coordination.
Key benefits and aspects of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
- Proactive Threat Mitigation: CTEM allows organizations to proactively identify and address security threats and vulnerabilities in real-time, reducing the window of exposure to potential attacks.
- Risk Reduction: By continuously assessing and prioritizing threats based on business impact and risk factors, organizations can allocate resources effectively to mitigate the most critical risks.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Implementing CTEM practices helps organizations improve their overall cybersecurity posture by focusing efforts on the most significant threats and vulnerabilities.
- Cost-Efficiency: CTEM helps organizations allocate resources efficiently by concentrating on vulnerabilities and threats that pose the greatest risk, reducing unnecessary spending on less critical areas.
- Compliance: Many regulatory standards and compliance frameworks require organizations to continuously monitor and manage security risks. CTEM helps organizations demonstrate compliance with these requirements.
- Improved Incident Response: By validating attack scenarios and response plans, CTEM ensures that organizations are well-prepared to respond effectively to security incidents when they occur.
- Business Continuity: CTEM practices help protect critical assets and systems, reducing the likelihood of security incidents that could disrupt business operations.
- Scope Definition: CTEM begins with defining the scope of an organization's attack surface, including both traditional and non-traditional assets such as social media accounts and supply chain systems.
- Discovery Process: An effective discovery process identifies visible and hidden assets, vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other risks within the defined scope.
- Threat Prioritization: Prioritization of threats is essential, considering factors like urgency, severity, availability of compensating controls, tolerance for residual risk, and the potential impact on the organization.
- Validation of Attack Scenarios: Organizations validate the exploitability of vulnerabilities and assess potential attack pathways to critical assets, ensuring that response plans are agile and robust.
- Mobilization of Resources: Communication and mobilization efforts are crucial to ensure that CTEM findings are operationalized, obstacles to approvals are minimized, and mitigation deployments are streamlined.
- Alignment with Business Goals: CTEM aligns security efforts with the organization's business goals by focusing on risks that have the greatest potential to impact business operations and reputation.
- Continuous Improvement: Organizations using CTEM continually refine their processes and responses based on insights gained from ongoing monitoring and threat assessments.
- Documentation and Reporting: Comprehensive documentation and reporting are integral to CTEM, providing insights for decision-makers and compliance purposes.
- Integration with Existing Security Measures: CTEM practices integrate with existing security tools and processes, enhancing an organization's overall security ecosystem.
- Ethical and Responsible Practices: CTEM emphasizes ethical and responsible security practices, ensuring that security research and response align with legal and ethical standards.
- Measurable Outcomes: CTEM should result in measurable improvements in an organization's security posture, reduced vulnerabilities, and enhanced incident response capabilities.
- Adaptability: CTEM is adaptable and scalable, accommodating the evolving security landscape and the changing needs of organizations over time.
CTEM aligns with the broader concepts of continuous monitoring and adaptive security, recognizing that cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing, dynamic process. By implementing CTEM practices, organizations aim to reduce the attack surface, minimize the window of exposure to threats, and respond swiftly to emerging cybersecurity challenges.
[ Download The IT Roadmap for Cybersecurity ]
To learn more about Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), visit the following link:
https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/how-to-manage-cybersecurity-threats-not-episodes