Physical security refers to the measures and practices implemented to protect physical assets, people, and property from unauthorized access, damage, theft, or other physical threats and incidents that can result in significant loss or harm to an organization. These threats encompass a range of events such as fire, floods, natural disasters, burglary, theft, vandalism, and acts of terrorism. Physical security focuses on creating a secure environment by employing various safeguards, controls, and procedures to mitigate risks and ensure the safety of individuals and assets.
By implementing a comprehensive framework of measures, physical security aims to establish a protected environment through the deployment of various safeguards, controls, and protocols. This proactive approach mitigates potential risks and ensures the well-being of people and valuable resources.
Central to physical security is the creation of layers of defense that collectively deter and counteract threats. These layers encompass access control systems, video surveillance, intrusion detection systems, security personnel, secure entry points, alarm systems, and perimeter fencing, among others. By integrating these components and practices, organizations can create a fortified environment that minimizes vulnerabilities and responds effectively to potential breaches. Physical security not only safeguards assets but also enhances the overall resilience of an organization, thereby fostering a safe and secure operating environment for employees, customers, and stakeholders.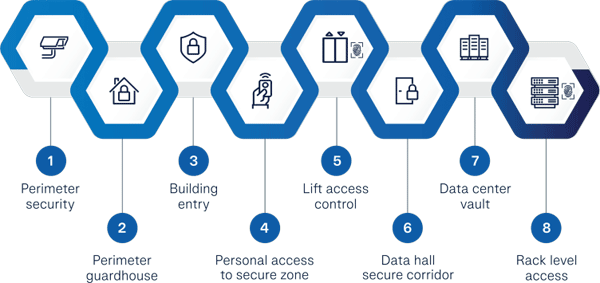
Physical security considerations
- Perimeter Security: Establish a secure perimeter around the data center facility using physical barriers such as fences, walls, gates, surveillance to control entry and access control systems. This ensures controlled entry and monitors access points.
- Suggested solution:
- Access Control Systems: LenelS2, HID Global, Gallagher
- Video Surveillance Systems: Axis Communications, Bosch Security Systems, Genetec
- Access Control Systems: LenelS2, HID Global, Gallagher
- Suggested solution:
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures using access cards, biometric systems, or other strong authentication mechanisms. This restricts entry to authorized personnel only and helps prevent unauthorized access.
- Suggested solution:
- Card Access Control Systems: HID Global, LenelS2, Johnson Controls
- Biometric Access Control Systems: Suprema, HID Global, Invixium
- Card Access Control Systems: HID Global, LenelS2, Johnson Controls
- Suggested solution:
- Surveillance Systems: Deploy comprehensive video surveillance systems throughout the data center facility, including server rooms and entrances. This allows for constant monitoring and recording of activities, enhancing security and providing valuable evidence in case of incidents.
- Suggested solution:
- IP Video Surveillance Systems: Axis Communications, Hikvision, Hanwha Techwin
- Video Management Systems: Genetec Security Center, Milestone XProtect, Avigilon Control Center
- IP Video Surveillance Systems: Axis Communications, Hikvision, Hanwha Techwin
- Suggested solution:
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Install intrusion detection systems (IDS) to promptly detect and alert against unauthorized access attempts or physical breaches. IDS can include sensors, alarms, and security monitoring tools that help identify potential security threats.
- Suggested solution:
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Bosch Security Systems, Honeywell, DSC
- Security Monitoring Tools: SolarWinds Security Event Manager, IBM QRadar, Splunk Enterprise Security
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Bosch Security Systems, Honeywell, DSC
- Suggested solution:
- Security Personnel: Employ trained security personnel responsible for monitoring access points, conducting patrols, and responding to security incidents. They play a crucial role in maintaining a secure environment and enforcing security policies and procedures.
- Suggested solution:
- Guard Tour Systems: TrackTik, GuardMetrics, Silvertrac Software
- Incident Reporting and Management Systems: Resolver, Omnigo Software, Silvertrac Software
- Guard Tour Systems: TrackTik, GuardMetrics, Silvertrac Software
- Suggested solution:
- Environmental Controls: Implement monitoring systems to manage environmental factors within the data center, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality. This helps ensure optimal conditions for equipment performance and prevents potential damage.
- Suggested solution:
- Environmental Monitoring Systems: AKCP, RLE Technologies, Vertiv
- Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) Solutions: Nlyte, Sunbird Software, Vertiv
- Environmental Monitoring Systems: AKCP, RLE Technologies, Vertiv
- Suggested solution:
- Fire Suppression Systems: Install advanced fire suppression systems, such as clean agent fire extinguishers or gas-based suppression systems, within the data center. These systems rapidly suppress fires without causing harm to sensitive equipment.
- Suggested solution:
- Clean Agent Fire Suppression Systems: FM-200 by Johnson Controls, ECARO-25 by Fike, Novec 1230 by 3M
- Gas-Based Fire Suppression Systems: Inergen by Johnson Controls, Argonite by Tyco, ProInert by Kidde
- Clean Agent Fire Suppression Systems: FM-200 by Johnson Controls, ECARO-25 by Fike, Novec 1230 by 3M
- Suggested solution:
- Redundant Power and Backup Systems: Implement redundant power sources, backup generators, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to ensure continuous power supply to critical infrastructure. This helps mitigate the risk of power outages and electrical failures.
- Suggested solution:
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems: APC by Schneider Electric, Eaton, Vertiv
- Backup Generators: Caterpillar, Cummins, Generac
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems: APC by Schneider Electric, Eaton, Vertiv
- Suggested solution:
- Seismic Design and Structural Reinforcement: Incorporate seismic-resistant designs and structural reinforcement in the construction of the data center facility. This helps minimize damage and ensure the integrity of the building during earthquakes or other seismic events.
- Suggested solution:
- Seismic Isolation Systems: Kinetics Noise Control, Dynamic Isolation Systems, Earthquake Protection Systems
- Seismic Bracing and Reinforcement: Simpson Strong-Tie, MiTek, Unistrut
- Seismic Isolation Systems: Kinetics Noise Control, Dynamic Isolation Systems, Earthquake Protection Systems
- Suggested solution:
- Flood Prevention Measures: Choose a data center location that is not prone to flooding, or implement flood prevention measures such as elevation or flood barriers. Implementing water detection systems helps identify and respond to water leakage or flooding within the facility.
- Suggested solution:
- Water Leak Detection Systems: RLE Technologies, Honeywell, Sensaphone
- Flood Barrier Systems: HESCO, FloodBreak, AquaFence
- Water Leak Detection Systems: RLE Technologies, Honeywell, Sensaphone
- Suggested solution:
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establish robust backup and disaster recovery mechanisms to ensure data integrity and availability. This includes regular data backups, replication to offsite locations, and comprehensive plans for restoring operations in the event of data loss or system failures.
- Suggested solution:
- Data Backup Solutions: Veeam, Commvault, Acronis
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Zerto, Druva, Carbonite
- Data Backup Solutions: Veeam, Commvault, Acronis
- Suggested solution:
- Vendor and Visitor Management: Enforce strict controls for third-party vendor access to the data center. Maintain a visitor log, issue temporary access badges, and enforce escort policies to monitor and control visitor activities within the facility.
- Suggested solution:
- Visitor Management Systems: Proxyclick, Traction Guest, Sine
- Access Control Systems with Visitor Management Features: Brivo, Paxton, Openpath
- Visitor Management Systems: Proxyclick, Traction Guest, Sine
- Suggested solution:
- Physical Redundancy: Implement redundant systems, such as power distribution units (PDUs) and cooling systems, to minimize the impact of single points of failure. This ensures the continuous operation of critical infrastructure in the event of component failures.
- Suggested solution:
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): Vertiv, APC by Schneider Electric, Eaton
- Redundant Cooling Systems: Vertiv, STULZ, Daikin
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): Vertiv, APC by Schneider Electric, Eaton
- Suggested solution:
- Cable Management: Properly manage and secure cabling infrastructure within the data center. This includes organizing and labeling cables, implementing cable management systems, and preventing accidental damage or unauthorized access to data and network connections.
- Suggested solution:
- Cable Management Solutions: Panduit, Chatsworth Products (CPI), Legrand
- Cable Labeling Systems: Brady, HellermannTyton, DYMO
- Cable Management Solutions: Panduit, Chatsworth Products (CPI), Legrand
- Suggested solution:
- Training and Awareness: Provide regular training to data center personnel on physical security procedures, emergency response protocols, and the importance of maintaining a secure environment. Foster a culture of security awareness among employees to mitigate risks and improve overall security posture.
- Suggested solution:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Cornerstone OnDemand, SAP Litmos, Docebo
- Security Awareness Training Platforms: KnowBe4, Proofpoint Security Awareness Training, Infosec IQ
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Cornerstone OnDemand, SAP Litmos, Docebo
- Suggested solution:
By implementing effective physical security measures, organizations can minimize risks, prevent unauthorized access, protect assets, and create a safer environment for employees, visitors, and valuable resources.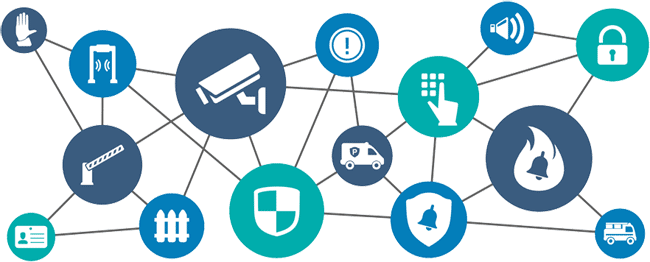
"Please note that the suggested technology solutions are among the best and widely used in the industry. However, it's important to evaluate them based on your specific requirements, budget, and compatibility with your data center infrastructure. Additionally, consult with experts and conduct proof-of-concept testing to determine the most suitable solutions for your data center's physical security needs."
How to Perform Physical Security Risk Assessment?
Performing a physical security risk assessment involves evaluating potential risks and vulnerabilities to physical assets, people, and operations within an organization. Here are the steps to conduct a physical security risk assessment:
- Identify Assets: Identify and document the physical assets that need protection, including facilities, equipment, data centers, sensitive information, and personnel.
- Threat Assessment: Identify potential threats that could impact the organization's physical security, such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, terrorist attacks, or insider threats. Consider both external and internal threats.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Assess vulnerabilities in the physical security infrastructure, processes, and controls. Identify weaknesses in areas such as access control, surveillance, perimeter security, environmental controls, and emergency response systems.
- Likelihood and Impact Analysis: Analyze the likelihood of each threat occurring and the potential impact it would have on the organization. Evaluate the consequences in terms of financial loss, operational disruptions, reputational damage, or harm to personnel.
- Risk Evaluation: Determine the level of risk associated with each threat by considering both the likelihood and potential impact. Prioritize risks based on their significance and the resources available for mitigation.
6. Mitigation Strategies: Develop and prioritize mitigation strategies to reduce or eliminate identified risks. Consider a combination of physical, procedural, and technological controls to address vulnerabilities and minimize the impact of threats. - Implementation: Implement the selected mitigation measures and controls. This may include installing security systems, enhancing access controls, improving surveillance, training personnel, or strengthening physical barriers.
- Testing and Evaluation: Regularly test and evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented security measures. Conduct drills, simulations, or vulnerability assessments to identify any gaps or weaknesses and refine the security posture accordingly.
- Documentation and Reporting: Document the findings, recommendations, and actions taken during the risk assessment process. Maintain a record of security policies, procedures, and incident response plans. Communicate the assessment results and mitigation measures to relevant stakeholders.
- Continuous Monitoring and Review: Physical security risks evolve over time, so ongoing monitoring and review are essential. Regularly assess the effectiveness of security measures, update risk assessments as needed, and adapt security strategies to address new threats or changes in the operating environment.
It is often beneficial to involve cross-functional teams, including security personnel, facility management, IT, and relevant stakeholders, in the risk assessment process to gain a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. Additionally, organizations may seek the assistance of external security consultants or experts to ensure a thorough and objective assessment.
Common Challenges of Physical Security
- Budget Constraints: Implementing comprehensive physical security measures can be costly. Organizations may face budgetary constraints that limit their ability to invest in state-of-the-art security technologies and infrastructure.
- Integration Complexity: Physical security systems often involve multiple components such as access control, video surveillance, intrusion detection, and fire suppression. Integrating these systems into a cohesive and effective security ecosystem can be complex and require expertise.
- Technological Advancements: Security threats and technology are constantly evolving. Staying updated with the latest security technologies and practices can be challenging, as organizations need to continuously adapt and upgrade their physical security systems to keep pace with new threats and advancements.
- User Convenience vs. Security: Striking a balance between user convenience and robust security measures can be a challenge. Strict security measures, such as extensive access control procedures, can inconvenience employees and impact operational efficiency if not implemented thoughtfully.
- Insider Threats: Physical security must address the risks posed by insider threats, including employees with malicious intent or those who inadvertently compromise security protocols. Safeguarding against insider threats requires a combination of access controls, monitoring, and employee awareness programs.
- Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities: New threats and vulnerabilities constantly emerge in the physical security landscape. This includes advancements in techniques for breaching physical barriers, compromising access controls, or exploiting vulnerabilities in security systems. Staying ahead of these threats requires proactive monitoring and continuous security assessments.
- Security Culture and Awareness: Building a culture of security awareness among employees and stakeholders is crucial. Educating individuals about security best practices, promoting a sense of responsibility, and fostering a security-conscious mindset can be challenging but is essential for effective physical security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations may be subject to industry-specific regulations and compliance standards related to physical security. Ensuring adherence to these requirements can be a challenge, as non-compliance may result in legal and financial consequences.
- Physical Vulnerabilities: Physical security measures are vulnerable to physical threats such as natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods), extreme weather events, or accidents. Mitigating these vulnerabilities requires careful facility design, robust infrastructure, and disaster preparedness plans.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Physical security systems require regular maintenance, upgrades, and testing to ensure they remain effective. Organizations must allocate resources and establish maintenance schedules to address potential system failures or vulnerabilities that may arise over time.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, effective risk management, ongoing investment in security technologies, employee training, and periodic security assessments to adapt to evolving threats and maintain a robust physical security posture.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_security
https://www.giac.org/paper/gsec/1402/data-center-physical-security-checklist/102617
https://www.isa.org/intech-home/2020/march-april/departments/physical-security-of-a-data-center
https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/Cybersecurity%20and%20Physical%20Security%20Convergence_508_01.05.2021_0.pdf